Biodiversity Risk Management
CAL focuses on and supports ecological conservation issues. Since 2011, we have organizing beach cleaning activities annually. In addition to earlier actions of shark fins embargo from 2014, CAL signed the "Buckingham Palace Declaration", as the only Taiwan airlines, to combat global illegal wildlife trade in endangered species and their products in 2017. In response to the focal points of recent international biodiversity issues, CAL further issued the "Forest and Biodiversity Commitment" in June 2022. This commitment has formulated CAL’s management strategies for forests and biodiversity, with the goals of no net loss of biodiversity and zero deforestation, and the strategies has been incorporated into corporate environmental governance and risk/opportunity management mechanism, platform and reporting process. We also adopted robust sustainable supply chain management approach, utilizing biodiversity assessment tools and biodiversity databases to identify and assess potential risk hotspots in CAL operation contexts and supply chains. Based on these assessments, we have develop appropriate measures to mitigate impacts with the enhancing engagement with stakeholders.

Biodiversity Risk Assessment
In order to assess the impact of biodiversity and dependence risks, CAL has taken the lead in the Taiwan's transportation industry to adopt the WWF’s tool of Biodiversity Risk Filter (BRF) in 2023, and employed various international biodiversity assessment tools or databases such as IBAT and ENCORE to evaluate risks associated with biodiversity across the 8 major categories and 33 specific aspects, encompassing physical, regulatory, reputational, and market risks. The assessment takes into account the characteristics of the industry, operation locations of CAL business and its critical partners, comprehensively considering their dependence on and impact to biodiversity. Based on the results of this assessment, CAL has formulated corresponding strategies and objectives.
Framework of BRF assessment tools
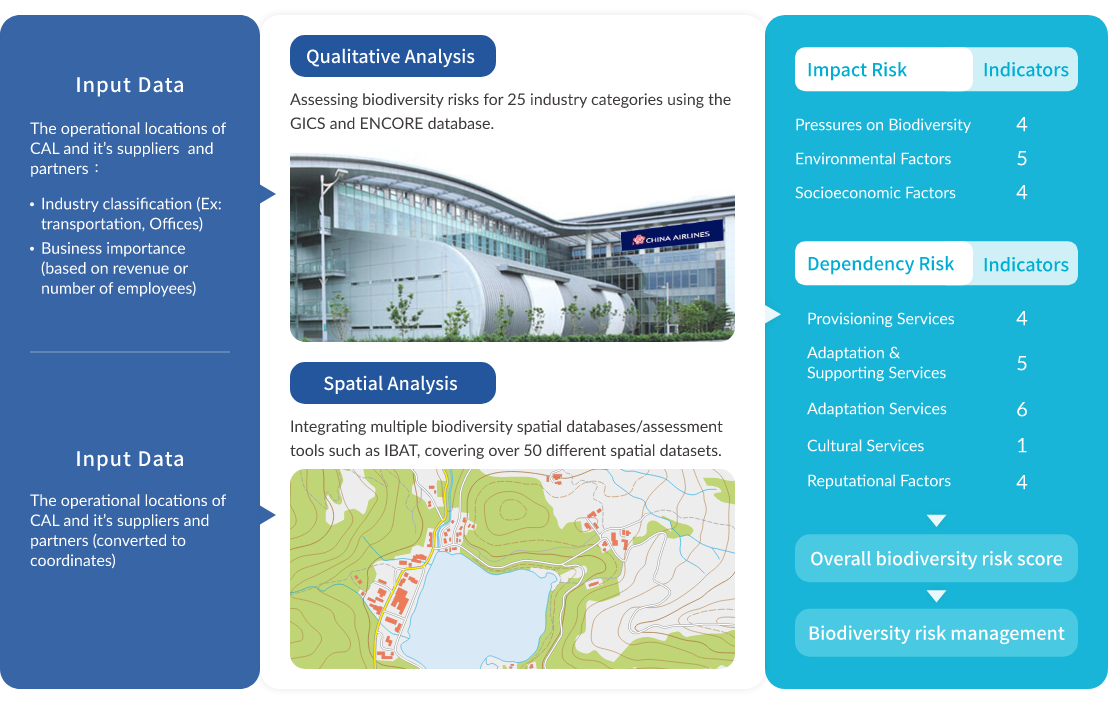
The results indicate that CAL's global operational locations and key value partners face a moderate level of comprehensive biodiversity risk in terms of dependence and impact. Among these risks, the dependence risk is relatively high for tropical cyclones, while in terms of impact risk, invasive species invasion and biodiversity pressures are relatively higher (moderate). However, the current BRF tool categorizes the aviation industry under the transportation services sector, which may have slight differences from the actual operations and potential impacts of an airline. China Airlines' main operational bases are located in airport areas, where strict adherence to airport management and government regulations is observed. Moreover, our business and sales locations are situated in downtown commercial areas, which may result in relatively lower local ecological and biodiversity impact risks.
In addition, we also utilized an integrated tool developed by the Taiwan Forestry Bureau, which serves as a local database, to validate the results obtained from BRF. By overlaying various spatial layers such as biodiversity hotspots, important wildlife habitats, wildlife protection areas, nature reserves, conservation areas, and state-owned forest enterprise zones, we assessed the biodiversity risks associated with our operational locations in Taiwan. The results showed that none of our Taiwan operational bases are located within or adjacent to the aforementioned areas.
Mitigation Hierarchy for Biodiversity
For the biodiversity risks identified through the BRF tool with higher significance, our company has employed a mitigation hierarchy approach (avoid, minimize, restore, compensate/offset) to deliberate on appropriate response strategies.
| Topic | Potential Risks | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Climate mitigation and adaptation | Tropical Cyclones A fully functioning ecosystem offers numerous benefits, including flood protection, drought mitigation, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through carbon sequestration. However, if the ecosystem collapses, the aviation industry’s operations will be affected by natural disasters such as landslides, forest fires, and asset losses resulting from typhoons/tropical cyclones. |
To effectively address the impacts of climate change, CAL has been the leading corporate in Taiwan’s' aviation industry to conduct greenhouse gas management and climate change mitigation and adaptation measures since 2008. CAL has further identified and disclosed climate-related financial risks and opportunities (including ecosystem services), and implement climate mitigation and adaptation measures with the guidelines of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in recent years. Additionally, CAL has partnered with Climate Impact Partners since 2018 to launch the "ECO Travel Carbon Offsetting" service (Please refer to Concern for Climate Change and TCFD for more details), and continuously supports initiatives and projects of important climate monitoring, mitigation, adaptation and biodiversity conservation, such as IAGOS/PGGM, Buckingham Palace, and Taiwan Carbon Sink etc. |
| Stringent transportation regulations | Invasive Species Invasion Illegal cross-border trading activities, particularly those involving wildlife or their parts, such as ivory and shark fins, pose significant risks as they traverse different ecosystems carrying various pathogens, parasites, and other organisms. These introduced invasive species often lack natural predators, allowing them to proliferate rapidly and pose threats to local ecosystems. Air transportation serves as one of the channels for cross-border illegal wildlife trafficking. |
CAL is the only transportation company in Taiwan that signed the "Buckingham Palace Declaration." CAL has committed to implementing a ban on the transportation of illegal wildlife since 2017. The CAL group completely prohibits the use of conservation animal and plant ingredients in its catering services, while also supporting ecological conservation projects. Additionally, we use the IATA assessment tools to regularly review the operational risks, and actively promote employee education and trainings to enhance operational awareness. |
| Robust environmental management | Biodiversity Pressures The operational bases of the aviation industry are primarily located in airports and urban areas. After site selection, environmental impact assessments, and mitigation measures, most of these areas do not fall under protected or ecologically sensitive regions. However, the development and operation of airport facilities and surrounding roads can cause moderate to medium levels of disturbance to biodiversity. Examples include noise from takeoff and landing processes, light pollution, and air pollution emissions. |
CAL has comprehensively promoted and continuously improved its corporate environmental and energy management system, and implemented risk control and environmental performance improvement measures to optimize the operational eco-efficiency (Please refer to Environmental Governance). We also follow the mitigation hierarchy method in line with the requirements of various stations, implement aircraft noise reduction and curfew operations to minimize the impact on biodiversity and the community. In addition, we actively promote activities such as afforestation, forest protection, beach cleaning, and support for ecotourism. Through restoration and compensatory measures to achieve the objective of zero net loss in biodiversity. Additionally, CAL collaborates with our group companies, such as Mandarin Airlines and Tigerair Taiwan, to collaborate on the "Taipei Zoo Kinmen Lesser Brown Scops Owl Egg Incubation Research Project", and actively participate in animal adoption programs to support the conservation efforts of indigenous species in Taiwan, including tigers, clouded leopards, and leopard cats. |